
-
Home
-
About Us
-
Products
-
News
-
Blog
-
Contact Us
Leave Your Message

Jaw crushers are essential in the mining and construction industries. Their ability to break down large rocks and materials makes them invaluable. When discussing the type of jaw crusher, it is crucial to understand the options available.
Different types of jaw crushers serve various applications and materials. For instance, some are designed for hard rocks, while others target softer materials. Each type has its unique features, which can impact efficiency. A deeper look into these classifications reveals not only their strengths but also their limitations.
Understanding the type of jaw crusher you need is vital for any project. It can determine the success of your operations. However, choosing the right one can be challenging. One must consider factors like material hardness, desired output size, and overall efficiency. Making the right choice involves reflection and a clear understanding of your specific needs.

Jaw crushers are essential in various industries, especially mining and construction. They come in different types based on design and construction. Understanding these types is crucial for efficient operation.
The two primary designs are the Blake and the Dodge jaw crushers. The Blake type features a fixed jaw and a moving jaw that swings about a pivot. This design allows for a more efficient crushing mechanism. According to industry reports, Blake crushers account for about 70% of the global market share. In contrast, Dodge jaw crushers have a variable discharge area. They are less common but useful for smaller operations due to their compact design.
Additionally, there is the Universal jaw crusher. This variant combines the features of both Blake and Dodge types, featuring a wider discharge area. It caters to diverse materials, making it suitable for various applications. A study indicated that many plants are shifting towards the Universal design for its versatility. However, not every operation may benefit from these advancements. Each design has its own set of efficiencies and limitations, requiring careful assessment before selection.
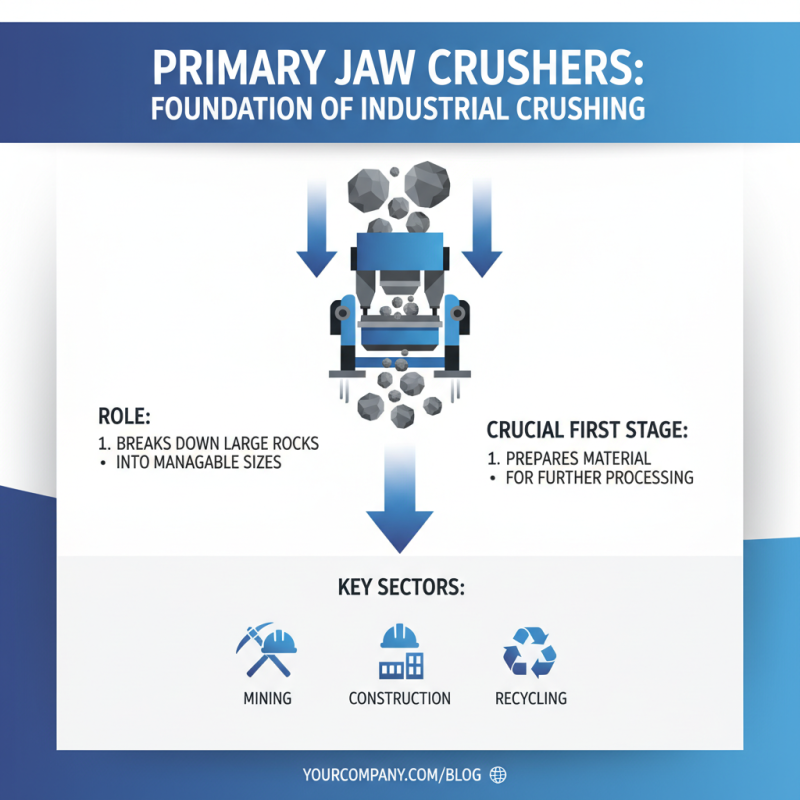
Primary jaw crushers play a pivotal role in various industries. They are essential for breaking down large rocks into manageable sizes. This initial stage of crushing is crucial for mining, construction, and recycling sectors.
In mining, primary jaw crushers handle hard materials. They process granite, basalt, and ores, reducing them to smaller particles. According to industry reports, about 70% of all crushing operations begin with a jaw crusher. Their efficiency in handling tough materials makes them indispensable.
The applications extend beyond mining. In construction, they crush concrete and asphalt. This recycling is vital for sustainable practices. A notable statistic shows that using recycled materials can reduce costs by up to 30%. Yet, some operators face challenges with wear and tear. Regular maintenance is essential but can be overlooked, leading to potential breakdowns.
In the world of mining and construction, secondary and tertiary jaw crushers play vital roles. These machines are engineered for tough tasks. They handle materials that have already been processed. Often, they are used to further crush rock. This leads to finer outputs, crucial for various applications. Operation usually includes reducing the size of large materials. For example, in the U.S. market alone, the demand for these crushers is projected to grow. Reports indicate a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) nearing 4.5% by 2027.
Secondary jaw crushers focus on high efficiency. They are capable of reducing extremely hard materials. The adjustment of the crusher's settings directly impacts the output size. However, operators sometimes face challenges. Misalignment can lead to uneven wear and inefficient crushing. Tertiary jaw crushers, on the other hand, are designed for precision. They create uniform sizes, which are essential for high-quality products. Proper maintenance is necessary. Professional insights reveal that up to 15% of operational delays stem from unplanned maintenance.
Combining both types can enhance production flow. However, careful consideration is needed in selection. The crush ratio, feed size, and desired final output must align. These complexities often require trial and error. Not every operation is smooth. With evolving technology, improvements in design and efficiency are within reach. Yet, companies must remain vigilant and adaptive.
When discussing jaw crushers, two main designs come into focus: single toggle and double toggle. Single toggle jaw crushers have a simpler structure. They use a moving jaw that operates on a single plane. This results in a more compact size. However, their design can limit the feed size. They generally produce a lower, but more consistent output.
On the other hand, double toggle jaw crushers offer distinct advantages. They have a more complex mechanism. This allows for greater crushing capacity and efficiency. The double toggle design aids in handling larger materials. It provides a more uniform quality of crushed products. Yet, this complexity can lead to maintenance challenges. Operators may need to invest in regular upkeep to prevent breakdowns. Choosing the right type depends on specific operational needs and circumstances. Each design has merits and weaknesses worth considering carefully.
Choosing the right type of jaw crusher is crucial for any industrial application. There are several types available, and understanding their use can significantly affect production efficiency. Factors influencing the choice include material hardness, throughput requirements, and operational costs. For example, a report by the Mining and Materials Research Institute indicates that high-capacity crushers are ideal for hard minerals, while smaller, more energy-efficient models work better with softer materials.
When selecting a jaw crusher, consider the mining operation's scale. Larger operations often benefit from heavy-duty models. Smaller operations may opt for equipment that offers lower initial costs but has higher maintenance rates. These choices can lead to trade-offs in efficiency and operational costs. Examine these factors carefully to avoid costly mistakes.
Tip: Assess the lifecycle cost of the jaw crusher, not just the purchase price. Maintenance and energy consumption can significantly impact long-term profitability.
Another factor is the crusher’s output size. Some industries require specific particle sizes. If the wrong type of jaw crusher is chosen, it may not produce the desired results. Always match the crusher's capabilities with your production needs. Misalignments here can lead to production bottlenecks.
Tip: Regularly review your operation’s needs. Adapting to changing demands can prevent inefficiencies from becoming entrenched.
| Jaw Crusher Type | Application | Capacity (ton/h) | Feed Size (mm) | Power (kw) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single Toggle Jaw Crusher | Medium to hard rocks, mining | 20-900 | 150-1200 | 15-200 |
| Double Toggle Jaw Crusher | Harder materials, large capacities | 50-1500 | 200-1500 | 50-500 |
| Cone Jaw Crusher | High hardness materials, abrasive | 30-1200 | 100-1000 | 30-400 |
| Mobile Jaw Crusher | Construction, demolition waste | 10-400 | 200-800 | 15-250 |
| Laboratory Jaw Crusher | Sample analysis, small batches | 0.1-10 | 30-100 | 2-5 |





